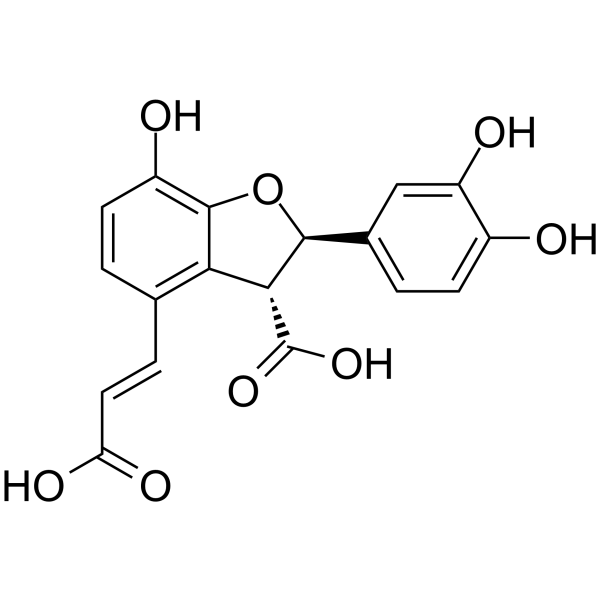
Przewalskinic acid A
CAS No. 136112-75-9
Przewalskinic acid A( —— )
Catalog No. M31445 CAS No. 136112-75-9
Przewalskinic acid A is a rare, water-soluble, and highly biologically active ingredient found, thus far, only in the Salvia przewalskii Maxim herb.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 640 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePrzewalskinic acid A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPrzewalskinic acid A is a rare, water-soluble, and highly biologically active ingredient found, thus far, only in the Salvia przewalskii Maxim herb.
-
DescriptionPrzewalskinic acid A is a rare, water-soluble, and highly biologically active ingredient found, thus far, only in the Salvia przewalskii Maxim herb.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number136112-75-9
-
Formula Weight358.3
-
Molecular FormulaC18H14O8
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (279.10 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Helospectin II
Helospectin II
-
Boc-11-aminoundecano...
Boc-11-aminoundecanoic acid is an Alkyl/ether-based?PROTAC linker?can be used in the synthesis of MS432.
-
56-Dimethylbenzimida...
Dimethylbenzimidazole is an intermediate in Riboflavin metabolism. Dimethylbenzimidazole is the second to last step for the synthesis of alpha-Ribazole.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


